Discover the thermal processes in the human body. Maintaining body temperature is a graceful dance choreographed by our thermoregulatory system.
This incredible system ensures that our body stays within a narrow temperature range despite external fluctuations.
Whether we are shivering in the cold or sweating on a hot day, our body is actively working to maintain thermal equilibrium.
The Building Blocks of Life: What is a Genome?
Understanding thermoregulation not only helps us to comprehend the amazing abilities of our body, but also gives us insight into various health conditions. By unraveling the mechanisms of thermoregulation, we can better understand how our body copes with extreme conditions, such as cold in winter or scorching heat in summer.

Thermal processes in the human body: the importance of maintaining body temperature
Maintaining an optimal body temperature is crucial for our overall well-being. Our bodies function best within a narrow temperature range, usually between 36 and 37 degrees Celsius (97-99 degrees Fahrenheit).
Deviating from this range can have serious consequences, affecting our physical and cognitive abilities. Whether it’s shivering in the cold or sweating in the heat, our bodies have clever mechanisms to restore and maintain thermal balance.
The thermoregulatory system is responsible for detecting changes in temperature and initiating appropriate responses to bring our bodies back into balance. It is a complex network involving various organs, including the skin, nervous system, and sweat glands. Without this system, we would be dependent on the environment and would not be able to function optimally in extreme conditions.
Thermoregulation system: how it works
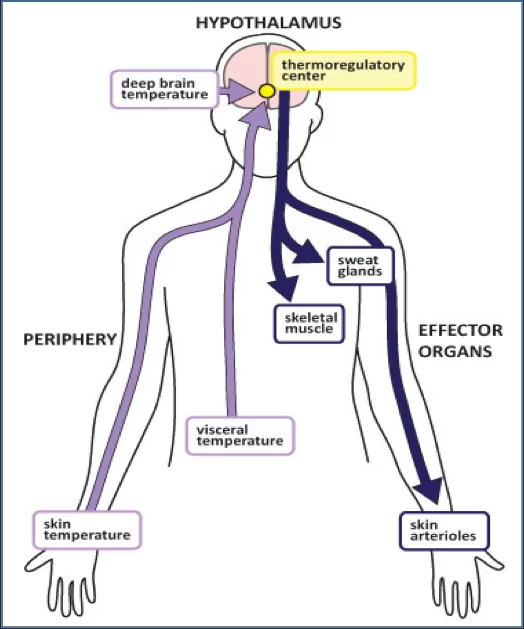
Thermal processes in the human body are built around the hypothalamus, a small area of the brain that acts as a control center. This tiny but powerful organ constantly monitors our blood temperature and receives information from temperature receptors located throughout the body. When the hypothalamus detects a deviation from the desired temperature range, it triggers a series of physiological reactions to restore balance.
One of the first lines of defense is the skin. As the largest organ in our body, it plays a crucial role in thermoregulation. When we are exposed to low temperatures, the blood vessels near the surface of the skin constrict, reducing blood flow and heat loss. This is why our extremities, such as fingers and toes, can feel cold to the touch. On the other hand, in the heat, blood vessels dilate, allowing for increased blood flow to the skin’s surface, promoting heat dissipation through sweat.
The role of the hypothalamus in thermoregulation
The hypothalamus acts as the conductor of our thermoregulatory orchestra. It receives signals from temperature receptors located throughout the body, including the skin, and interprets this information to determine the appropriate response. When the hypothalamus detects a drop in body temperature, it initiates shivering, the rapid contraction and relaxation of muscles to generate heat and keep the body warm.
Shivering is an involuntary response, often accompanied by teeth chattering, that helps us fight off the cold and maintain our body temperature in the optimal range.
On the other hand, when the hypothalamus senses that the body is getting too warm, it activates the sweat glands. Sweat consists mainly of water, with a small amount of electrolytes and waste products. When sweat evaporates from the surface of the skin, it cools the body, preventing overheating. This is why we often feel sweaty during intense physical activity or on hot summer days.
Factors affecting heat processes in the human body
Although the thermoregulatory system is highly efficient, there are several factors that can affect our body’s ability to regulate temperature. External factors such as ambient temperature and humidity play a significant role.
In hot and humid environments, it is harder for our bodies to dissipate heat through sweat evaporation, making us more susceptible to heat exhaustion or heat stroke.
Likewise, in cold environments, our bodies may struggle to generate enough heat through shivering, leading to hypothermia.
Individual factors such as age, gender, and overall health also affect thermoregulation. Infants and the elderly, for example, have a harder time regulating their body temperature due to underdeveloped or decaying thermoregulatory mechanisms.
Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disease or diabetes, can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate temperature properly. It is important to be aware of these factors and take appropriate measures to maintain a comfortable and safe body temperature.
Thermoregulation and homeostasis
Thermoregulation is closely related to the concept of homeostasis – the body’s ability to maintain stable internal conditions despite external fluctuations.
Homeostasis is essential for our survival, as it ensures the optimal functioning of our cells. Temperature regulation is just one aspect of homeostasis, along with other variables such as blood pressure, pH, and electrolyte balance. The thermoregulatory system works in harmony with other body systems to maintain overall balance and keep us healthy.
Common disorders and conditions of thermoregulation
Although our bodies are generally good at thermoregulation, certain disorders and conditions can disrupt this delicate balance. For example, hypothermia occurs when the body loses heat faster than it can produce it, resulting in a dangerously low body temperature.
Symptoms include shivering, confusion, and eventual loss of consciousness. On the other hand, hyperthermia, or heat stroke, occurs when the body is unable to cool itself and overheats. It is characterized by high body temperature, rapid breathing, and confusion.
Other conditions, such as Raynaud’s disease, disrupt blood flow to the extremities, causing the hands and feet to become cold even at moderate temperatures. Similarly, hyperhidrosis causes excessive sweating, which often interferes with daily activities and causes social discomfort.
Understanding these disorders can help people seek appropriate treatment and effectively manage their symptoms.
How to help the body regulate temperature
Although our bodies have complex mechanisms for regulating temperature, there are steps we can take to support this process.
It is very important to dress appropriately for the weather. In cold weather, layered clothing helps to keep heat closer to the body, while in hot weather, clothing made of breathable fabrics that fit loosely around the body promotes better air exchange and sweat evaporation. It is also important to maintain a water balance, as water is essential for sweating and cooling.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can also contribute to optimal thermoregulation. Exercise helps improve circulation, increasing the body’s ability to distribute heat evenly. A good diet provides the body with the necessary energy and nutrients for optimal functioning, including thermoregulation.
Thermal processes in the human body in extreme conditions
Our bodies are remarkably adaptable to extreme conditions, allowing us to survive and thrive in conditions that would otherwise be unbearable. For example, in cold climates, our bodies undergo physiological changes to keep warm.
Blood vessels near the skin constrict, reducing blood flow to the extremities and redirecting it to vital organs. This can cause the hands and feet to feel cold, but it helps to maintain the overall body temperature.
In hot environments, our bodies rely on sweating to cool down.
As sweat evaporates from the surface of the skin, it dissipates heat, helping to maintain a safe body temperature. However, prolonged exposure to extreme heat can overwhelm the body’s cooling mechanisms, leading to heat-related illnesses. Understanding how our bodies react to extreme conditions can help us take the necessary precautions and protect ourselves.
Conclusion: understanding the complexity of the thermoregulation system
Thermal processes in the human body and the human thermoregulatory system are a marvel of biological engineering. From the skin to the hypothalamus to the sweat glands, each component plays a crucial role in maintaining body temperature within a narrow range.
Understanding the intricacies of thermoregulation not only deepens our understanding of our own bodies, but also provides insight into various health conditions and how to overcome them.
The next time you shiver in the cold or feel the sweat break out on a hot day, stop and think about the incredible ways our bodies adapt and keep us comfortable. Our thermoregulatory system is a testament to the wonders of nature and the amazing abilities of the human body.



